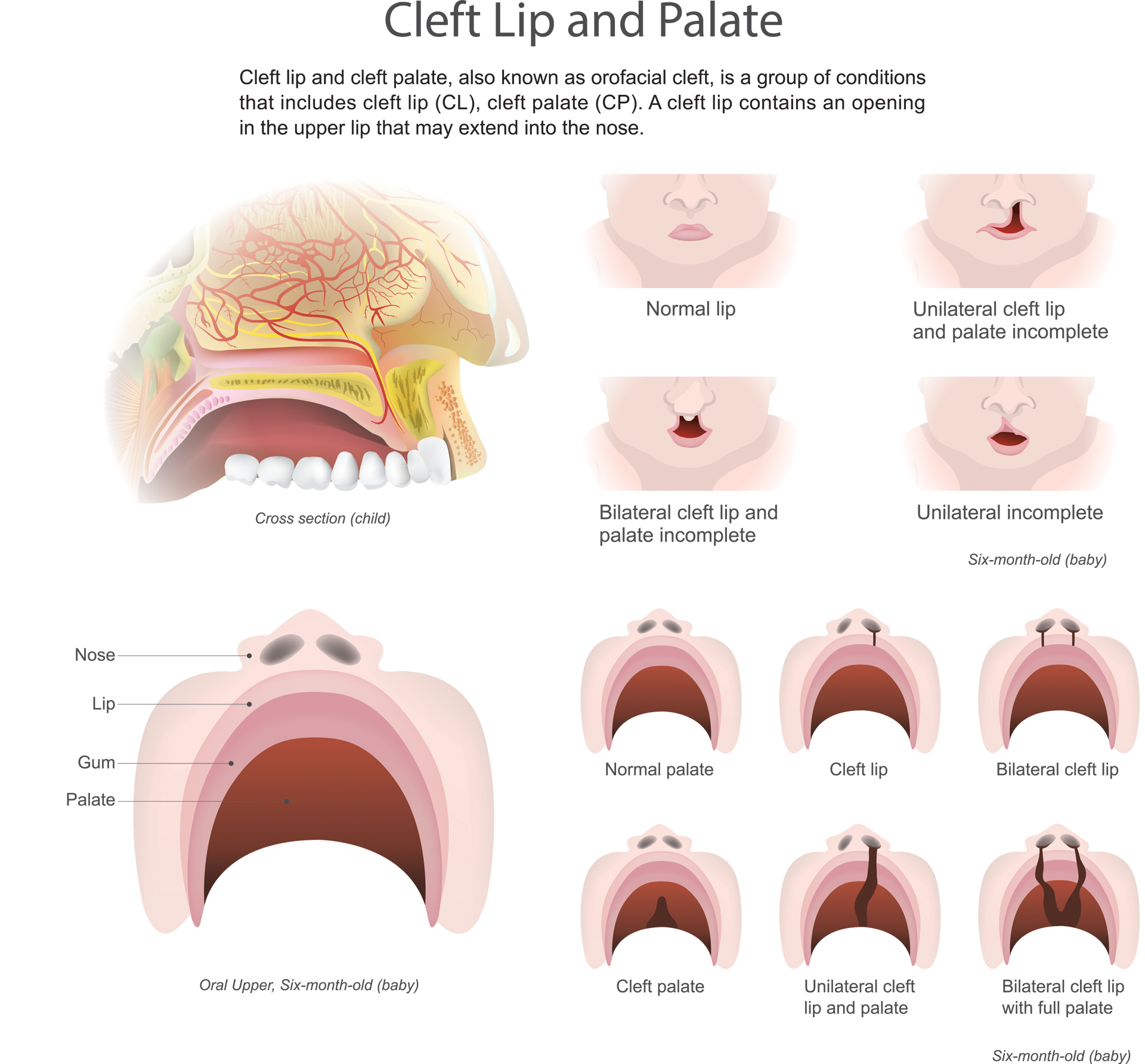
During early pregnancy, separate processes of the fetal face develop individually and then join together, including the left and right sides of the roof of the mouth and lips. However, if some parts do not join properly, sections don’t meet and the result is a cleft. If the separation occurs in the upper lip, the child is said to have a cleft lip. A completely formed lip is important not only for a normal facial appearance but also for sucking and to form certain sounds made during speech. A cleft lip is a condition that creates an opening in the upper lip between the mouth and nose. It looks as though there is a split in the lip. It can range from a slight notch in the colored portion of the lip to complete separation in one or both sides of the lip extending up and into the nose. A cleft on one side is called a unilateral cleft. If a cleft occurs on both sides, it is called a bilateral cleft. A cleft in the gum may occur in association with a cleft lip. This may range from a small notch in the gum to a complete division of the gum into separate parts. A similar defect in the roof of the mouth is called a cleft palate.
The palate is the roof of your mouth. It is made of bone and muscle and is covered by a thin, wet skin that forms the red covering inside the mouth. You can feel your own palate by running your tongue over the top of your mouth. Its purpose is to separate your nose from your mouth. The palate has an extremely important role during speech because when you talk, it prevents air from blowing out of your nose instead of your mouth. The palate is also very important when eating. It prevents food and liquids from going up into the nose. As in cleft lip, a cleft palate occurs in early pregnancy when separate areas of the face do not join together properly. A cleft palate occurs when there is an opening in the roof of the mouth. The back of the palate is called the soft palate and the front is known as the hard palate. A cleft palate can range from just an opening at the back of the soft palate to a complete separation of the entire roof of the mouth (soft and hard palate). Since the lip and palate develop separately, it is possible for a child to be born with a cleft lip, palate or both. Cleft defects occur in about one out of every 800 babies. Children born with either or both of these conditions usually need the skills of several professionals to manage the problems associated with the defect such as feeding, speech, hearing and psychological development. In most cases, surgery is recommended.
Cleft lip surgery is performed in early infancy. The goal of surgery is to close the separation, restore muscle function, and provide a normal shape to the mouth. The nostril deformity may be improved as a result of the procedure or may require a subsequent surgery.
A cleft palate is initially treated with surgery usually when the child is between 7 to 18 months old. The major goals of surgery are to:
There are many different techniques that surgeons will use to accomplish these goals. The choice of techniques may vary between surgeons and should be discussed between the parents and the surgeon prior to the surgery. The cleft alveolus in the dental arch is generally repaired between the ages of 7 and 12 when the cuspid teeth begin to develop. Procedures for revision and refinement are often done at various periods throughout growth. The procedure involves placement of bone from the hip into the bony defect, and closure of the communication from the nose to the gum tissue in layers. It may also be performed in teenagers and adults as an individual procedure or combined with corrective jaw surgery.
Frequently the growth and development of the upper jaw may be deficient, creating a disparity between the upper and lower jaws. In these instances, in the teenage years improves jaw function and facial appearance.
Dr. Tamimi and team at Royal Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery are trained in such complex procedures and surgeries with the appropriate experience, the team ensures all patients questions are answered and understands the anxieties that can accompany a patient or a parent when dealing with such procedures.